
You can also query the 8dot3 name behavior by using the 8dot3name subcommand.
#Fsutil disabledeletenotify how to#
Silent deletion of data when the system encounters corruption on an NTFS volume.įile-delete notification (also known as trim or unmap)įor examples of how to use this command, see Examples. The size of the master file table zone (MFT Zone) The frequency with which quota events are written to the system log and to NTFS paged pool and NTFS non-paged pool memory cache levels The updating of the Last Access Time stamp when directories are listed on NTFS volumes The creation of 8.3 character-length file namesĮxtended character use in 8.3 character-length short file names on NTFS volumes Queries or sets NTFS volume behavior, which includes:
#Fsutil disabledeletenotify windows 8#
Windows 8.x and 10.x) do not support the DisableDeleteNotify parameter.Applies To: Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2003 R2, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2000, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows 8 Note 3: Non-server versions of Windows (e.g. All earlier versions (e.g Windows 2008) do not have the same issue. Note 2: Only Windows Server 2012 and later Hosts are affected. This attribute is configurable for NTFS and ReFS volumes. Earlier versions of SANsymphony will prevent the Windows Host from sending the commands. fsutil behavior query disabledeletenotify A result of zero means the attribute is enabled. If the output is DisableDeleteNotify 1, then TRIM is disabled. If the output is DisableDeleteNotify 0, then TRIM is enabled.
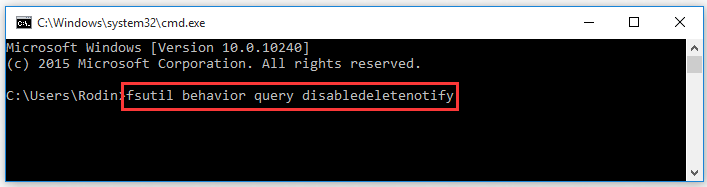
Note 1: Only Virtual Disks served from 9.0 PSP4 or greater support the SCSI Trim and Unmap feature. You can check if TRIM is enabled on your Windows computer by opening the Command Prompt and typing in the command fsutil behavior query DisableDeleteNotify. DisableDeleteNotify=1 - indicates the 'Trim and Unmap' feature is on (disabled).(Na pierwszy rzut oka jest to troch zagmatwane - przy wartoci 0 opcja DisableDeleteNotify jest wyczona. Wszystko jest w porzdku i nie musisz si tym martwi. Jeli zobaczysz DisableDeleteNotify 0, TRIM jest wczony. And you can use the following command to verify the current setting of NTFS and ReFS: fsutil behavior query disabledeletenotify. fsutil behavior set DisableDeleteNotify ReFS 1.

Ive read about disabling the UNMAP feature with the following commands: fsutil behavior set DisableDeleteNotify NTFS 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
